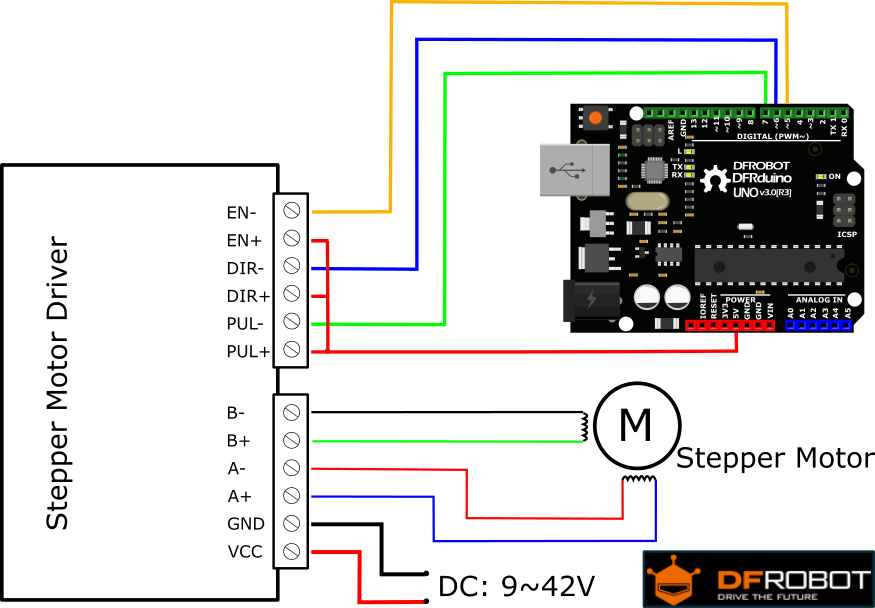
Stepper motor with TB6000 Microstep driver
We have the 42BYGHM809 Stepper motors with the TB6600 Stepper motor microstep driver to the Arduino using the BasicStepperDriver.h library.
-
Download and install the driver to arduino from here. (If you need help, check the manual library installation wiki page here).
-
Try this stepper Motor 42BYGHM809 / TB6600 Test Program note the steps are 14000 for a 360 turn.
/*
* Simple demo, should work with any driver board
*
* Connect STEP, DIR as indicated
*
* Copyright (C)2015-2017 Laurentiu Badea
*
* This file may be redistributed under the terms of the MIT license.
* A copy of this license has been included with this distribution in the file LICENSE.
*/
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "BasicStepperDriver.h"
// Motor steps per revolution. Most steppers are 200 steps or 1.8 degrees/step
#define MOTOR_STEPS 14000
#define RPM 120
// Since microstepping is set externally, make sure this matches the selected mode
// If it doesn't, the motor will move at a different RPM than chosen
// 1=full step, 2=half step etc.
#define MICROSTEPS 1
// All the wires needed for full functionality
#define DIR 6
#define STEP 7
//Uncomment line to use enable/disable functionality
//#define SLEEP 13
// 2-wire basic config, microstepping is hardwired on the driver
BasicStepperDriver stepper(MOTOR_STEPS, DIR, STEP);
//Uncomment line to use enable/disable functionality
//BasicStepperDriver stepper(MOTOR_STEPS, DIR, STEP, SLEEP);
void setup() {
stepper.begin(RPM, MICROSTEPS);
// if using enable/disable on ENABLE pin (active LOW) instead of SLEEP uncomment next line
// stepper.setEnableActiveState(LOW);
}
void loop() {
// energize coils - the motor will hold position
// stepper.enable();
/*
* Moving motor one full revolution using the degree notation
*/
stepper.rotate(360);
/*
* Moving motor to original position using steps
*/
stepper.move(-MOTOR_STEPS*MICROSTEPS);
// pause and allow the motor to be moved by hand
// stepper.disable();
delay(5000);
}